CRM Software Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide is your key to unlocking the secrets behind selecting the best CRM solution for your business without breaking the bank. In a landscape filled with endless options and pricing structures, understanding how costs add up and what truly matters allows you to make confident, strategic decisions for your organization.
From exploring tailored features and pricing models to exposing hidden fees and sharing real-world case studies, this guide covers everything you need to navigate CRM pricing with clarity. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large enterprise team, you’ll find practical tips, tables, and advice to help align your CRM investment with your business goals and budget, giving you the edge to choose wisely and maximize value.
Introduction to CRM Software Pricing
CRM software pricing plays a crucial role for organizations of all sizes when choosing the right customer relationship management solution. Understanding how much you need to invest helps businesses align their CRM strategies with broader financial planning, ensuring a good fit for both current operations and future growth. CRM pricing can often appear complex at first glance, but breaking down the structure and knowing what factors influence costs can make decision-making much smoother.
Several elements determine the price tag attached to CRM software. These range from user license counts and feature sets to the level of customization and integration possibilities. Additionally, CRM vendors use various pricing models that could suit different business scenarios. Knowing the industry standards and pricing mechanisms allows companies to select solutions that not only meet their requirements but also provide optimal value for investment.
Factors Shaping CRM Software Pricing Structures
CRM pricing structures are heavily influenced by a mix of technical, operational, and organizational factors. Businesses should pay close attention to how these aspects might impact the final cost, whether they’re a startup, mid-sized firm, or an enterprise player. Among the most significant factors are the number of users, the depth of features provided, integration capabilities, and ongoing support levels.
More advanced features, such as automation, advanced analytics, or industry-specific modules, can drive prices upward. Meanwhile, options for customization and seamless integration with existing business tools are often priced as premium add-ons. Finally, the quality and availability of technical support are significant, as high-end support packages usually incur extra charges.
Key Factors Influencing CRM Pricing
Several key elements directly affect the cost of CRM software. Recognizing these can help organizations anticipate their true investment and avoid budget surprises down the road. For most businesses, the main cost drivers involve the number of users, level of customization, included features, integration scope, and available support.
Breakdown of Pricing Determinants
Customization, user count, and feature sets are among the most impactful elements shaping CRM costs. The table below illustrates how these factors contribute to final pricing structures:
| Element | Description | Impact on Pricing | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Count | Total number of employees accessing the CRM | Price increases with more users | Startup (5 users) pays less than enterprise (100+ users) |
| Customization | Adjusting workflows, fields, or dashboards to fit unique needs | Heavily customized platforms are pricier | Custom-coded sales pipeline vs. standard template |
| Features | Core vs. advanced functionalities | Premium features add to base cost | Lead scoring or AI analytics as add-ons |
| Integration | Connecting CRM with other business tools | Complex integrations may require higher-tier plans | Integration with ERP or third-party marketing platforms |
Influence of Integration Capabilities and Support
Integration and support are frequently underestimated when budgeting for CRM software. Seamless integration with legacy or third-party systems often necessitates middleware or additional API usage, both of which can carry extra charges. Moreover, ongoing support—ranging from basic email troubleshooting to 24/7 premium phone support—can significantly alter the total cost of ownership. High-touch support is especially valuable for organizations with limited in-house IT expertise, but it typically comes at a higher price point.
Popular CRM Pricing Models
CRM vendors offer several different pricing models, each catering to unique business preferences and cash flow strategies. Understanding the structure of these models is essential for companies aiming to match their software investment with their organizational needs and growth trajectory.
Overview and Comparison of CRM Pricing Approaches
The most common CRM pricing models include subscription-based, one-time license, tiered, and freemium options. Each model provides particular advantages and trade-offs depending on use cases and business objectives.
| Model | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subscription-based | Recurring monthly or annual payments per user or organization | Lower upfront costs, regular updates, scalable | Long-term costs may exceed one-time purchases; dependent on vendor’s ongoing viability |
| One-time License | Single upfront payment for perpetual software use | No recurring fees, full ownership | Large initial investment, may lack updates/support |
| Tiered | Multiple pricing levels based on features or usage limits | Flexible, pay for what you need | Feature restrictions at lower tiers; upgrades may be necessary as needs grow |
| Freemium | Basic features available for free, with premium add-ons | Risk-free trial, easy adoption for small teams | Limited functionality unless upgrading; potential for hidden costs |
Suitable Use Cases for Each Model
Subscription-based pricing is ideal for startups and growing companies that prefer spreading their costs over time and need the latest features. One-time licensing is more appropriate for established organizations looking to minimize recurring expenses and have in-house IT support for maintenance. Tiered models work well for businesses that anticipate scaling usage or feature requirements as they grow, while freemium options are best suited for small teams or early-stage ventures wanting to explore CRM capabilities before committing to a paid plan.
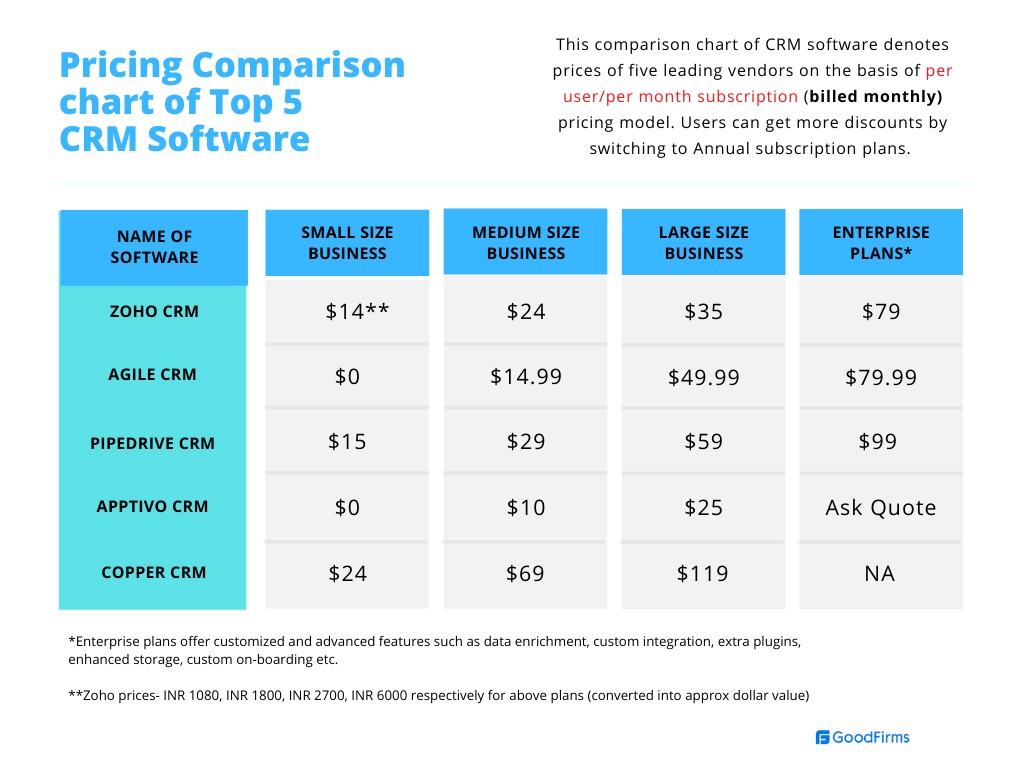
CRM Software Pricing Comparison Table
A clear side-by-side comparison of leading CRM solutions allows businesses to quickly assess which platform best aligns with their budget, required features, user capacity, and contract preferences. The table below Artikels the main distinctions among top CRM offerings:
| CRM Solution | Starting Price per User/Month | Key Features | Contract Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | $25 | Sales automation, custom workflows, analytics | Monthly/Annual, scaling plans |
| HubSpot CRM | Free / $45 (Starter) | Contact management, reporting, integrations | Free tier, no contracts, upgrade anytime |
| Zoho CRM | $14 | Omnichannel comms, automation, AI predictions | Flexible contracts, scalable tiers |
| Pipedrive | $21 | Pipeline management, email integration | Monthly/Annual options, easy cancellation |
Interpreting this table requires considering not only the base price but also which features are essential for your business operations. Some vendors offer powerful tools at higher price points, while others provide free tiers with upgrade paths as needs evolve. Also, contract flexibility can impact your ability to scale up or down without facing penalties or locked-in costs.
Be aware that initial quoted prices rarely include all potential expenses. Hidden costs—such as premium integrations, advanced analytics, or extra support—can substantially increase the total cost of ownership over time.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of CRM Solutions
Evaluating CRM investments goes beyond sticker prices—it’s about weighing the value gained from improved efficiency, customer insights, and revenue against the total expenditure. Approaching this process methodically ensures that organizations make informed, data-driven decisions that support long-term growth.
Measuring Value Relative to CRM Investment
Cost-benefit analysis involves calculating both tangible and intangible returns from CRM adoption. While direct ROI calculations focus on increased sales or reduced administrative hours, qualitative gains such as better customer satisfaction and process transparency also matter. Organizations should track metrics before and after CRM implementation to pinpoint specific improvements attributable to the software.
Practical ROI Calculation Examples
For instance, a small company investing $2,000 annually in CRM software might see a $10,000 increase in annual sales due to better lead management, yielding a 400% ROI. In a larger enterprise, a $50,000 CRM investment could reduce customer churn by 10%, saving hundreds of thousands in recurring revenue.
Industry-Specific Cost-Benefit Procedures, CRM Software Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide
Different industries should tailor their cost-benefit analysis to relevant KPIs. Retailers may focus on metrics like cart abandonment or repeat purchase rates, while B2B service providers might prioritize deal cycle times or customer lifetime value. Outlining these measurements in advance, and comparing them with CRM-driven improvements, ensures precise evaluation of software value.
Additional Fees and Hidden Costs in CRM Pricing
Beyond visible monthly or annual fees, implementing a new CRM often involves less obvious expenses that can materially impact your budget. Understanding these potential charges early on ensures smoother financial planning and a more accurate picture of total cost.
Categories of Extra CRM Costs
The following bullet list highlights some of the most common additional fees associated with CRM use:
- Onboarding or setup fees
- Customization and development charges
- Training for users and administrators
- Premium or priority support packages
- Data migration services
- API access or integration surcharges
- Additional storage costs
Onboarding often includes initial data loading and system configuration, which some vendors charge as a one-time fee. Customization and development work—especially for complex business processes—can quickly escalate costs. Training ensures your team can fully leverage CRM features, but may not be bundled in base plans.
Premium support is frequently priced as an add-on, granting access to faster response times or dedicated account managers. Data migration and API access, especially for companies moving from legacy systems or seeking deep integrations, are other common sources of extra charges. Monitoring usage and understanding where surcharges might apply helps prevent unwelcome surprises.
Tips for Selecting CRM Software Based on Pricing
Selecting CRM software involves balancing functional requirements with budget constraints. Making savvy choices ensures your organization gets the best possible return on investment while avoiding costly missteps.
Effective Evaluation Strategies
It’s important to align CRM selection with both financial realities and operational needs. This involves detailed needs assessment, careful comparison shopping, and thoughtful negotiations with vendors. Don’t be afraid to ask for detailed breakdowns of costs and to seek references or case studies from similar companies.
Negotiating pricing or requesting discounts is a common and accepted practice; many vendors are willing to work with you, especially for longer contracts or larger user counts.
- Always request a full breakdown of all potential costs, including one-time and recurring fees.
- Ask for a trial period or proof-of-concept to test real-world fit before committing.
- Leverage competitive offers to negotiate better pricing or added features.
- Clarify upgrade or downgrade terms to avoid future contract lock-ins.
- Document every agreement, especially regarding customizations or add-ons.
Best practices for requesting transparent pricing include asking for itemized quotes, inquiring about volume or annual discounts, and seeking clear explanations of all additional fees. Being proactive about these points helps ensure a smooth selection process and better long-term value.
Real-World Case Studies: CRM Pricing Decisions: CRM Software Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide
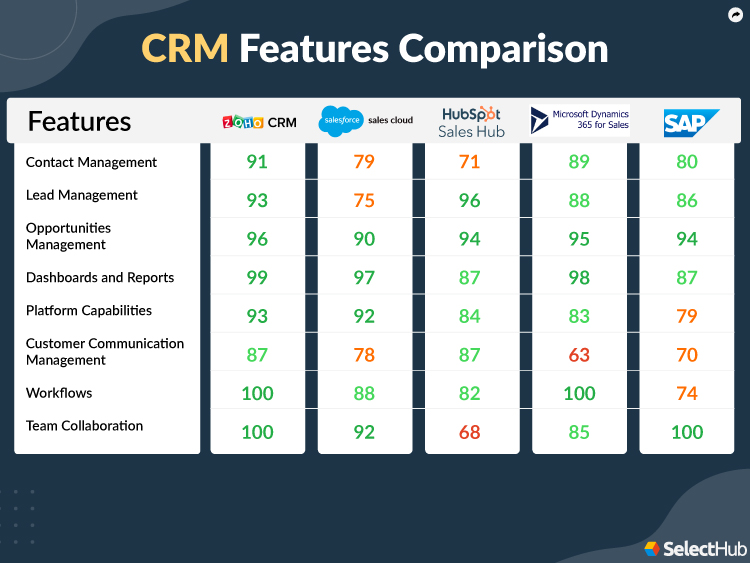
Learning from peers who have already navigated the CRM selection process can provide valuable insights for your own decision-making. Many organizations have found meaningful ways to balance pricing considerations with functional requirements.
Examples of Successful CRM Selection
A SaaS startup with 20 employees compared several CRM providers, ultimately choosing a subscription-based solution that offered a scalable plan starting at $20/user/month. Their selection process involved mapping out user requirements, requesting detailed quotes, and trialing top contenders. By forecasting user growth and negotiating a multi-year agreement, they secured a 15% discount and free onboarding.
A midsize retail chain needed advanced inventory integration and opted for a tiered CRM model. By quantifying expected cost savings from automation and improved cross-channel reporting, they justified the higher-tier price and avoided overpaying for features they didn’t need.
“Pricing transparency was the deciding factor. We could clearly see where our money was going, and the vendor’s willingness to tailor the contract to our needs made all the difference.”—Head of Operations, Retail Chain
These real-world decisions highlight the importance of thorough needs analysis, open vendor communication, and strategic negotiation in achieving the best value from a CRM investment.
Glossary of Common CRM Pricing Terms
The CRM world comes with its own set of pricing jargon. Understanding these terms empowers buyers to compare solutions with confidence and avoid unexpected fees along the way.
Essential Pricing Terminology Explained
Below is a list of frequently used CRM pricing terms and their definitions:
- Per-user pricing: Charging structure where a fee is assessed for each active user or seat on the platform.
- Add-ons: Optional extra features or modules not included in the core package, often available for an additional fee.
- API calls: Interactions made between the CRM and external systems via the Application Programming Interface, which may be subject to limits or extra charges.
- Storage limits: Defined caps on how much data (contacts, files, emails) can be stored within the CRM before incurring overage fees.
- Onboarding fee: One-time setup or implementation charge to get the CRM up and running for your organization.
- Contract flexibility: The degree to which a customer can adjust, upgrade, or exit a contract without penalties.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): A software delivery model where CRM is hosted in the cloud and accessed via subscription, rather than installed on-premise.
Knowing these terms will help you communicate more effectively with vendors and make smarter, more informed CRM purchasing decisions.
Last Recap
In summary, navigating CRM Software Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide equips you with the essential knowledge to make smart, informed choices in your CRM journey. By understanding the variables that drive costs, learning to spot hidden fees, and using proven evaluation strategies, you can confidently select a CRM solution that fits your needs today and supports your growth tomorrow.
FAQ Guide
What are the main differences between free and paid CRM solutions?
Free CRM options often come with basic features and limited user support, while paid versions provide advanced functions, more customization, integrations, and dedicated support for businesses with greater needs.
Can CRM software pricing be negotiated with vendors?
Yes, many CRM vendors are open to negotiating pricing, especially for larger contracts or longer-term agreements. It’s always a good idea to ask for discounts or custom packages that fit your requirements.
Is it possible to upgrade or downgrade CRM plans easily?
Most CRM providers offer flexible options to upgrade or downgrade your plan as your business needs change, but it’s important to review contract terms for any potential fees or restrictions.
How often do CRM software prices change?
CRM software prices can change annually or in response to new features, industry shifts, or promotional periods. It’s wise to monitor your vendor’s pricing announcements and review your contract terms regularly.
Do CRM pricing plans usually include customer support?
Basic customer support is often included in entry-level plans, but premium or priority support may require additional fees or higher-tier subscriptions.
